Table of contents
Introduction
Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT have shown tremendous potential in enhancing productivity across various domains. However, these models are limited to the knowledge they were pretrained on. To adapt LLMs to our specific needs, we often need to provide them with custom knowledge or data. For example, how would an LLM answer a question like "When was Albert Einstein born?" without access to any biographical information?
One possible solution is to fine-tune the LLM on a large corpus of documents that contain relevant knowledge. However, this approach has some drawbacks. Fine-tuning can cause the LLM to forget its pre-trained knowledge or hallucinate facts that are not supported by evidence. Fine-tuning also reduces the flexibility and control of the LLM, as it becomes dependent on a fixed set of documents.
A more promising alternative is to use a retrieval-augmented language model (REALM). A REALM is a method that integrates a knowledge retriever into an LLM, allowing it to dynamically access and reason over external documents as supporting knowledge for answering questions.
In this blog post, we'll explore three primary methods to ingest custom knowledge:
Building your own model from scratch with a custom dataset
Fine-tuning an existing model with a custom dataset
Implementing a Retrieval-Augmented Language Model (REALM)
We'll briefly discuss the pros and cons of each method and then dive deeper into the implementation of a Retrieval-Augmented Language Model.
Method 1: Building Your Own Model from Scratch
This involves gathering data, cleaning and preprocessing it, then training a model using self-supervised learning techniques like masked language modeling. While this results in a model tailored to your data, it requires immense compute resources and time to train a performant LLM.
Pros ✅:
Complete control over the architecture and training data
Can be tailored to very specific domains or tasks
Cons ❌:
Requires substantial resources, such as computational power and data
Time-consuming and complex process
Method 2: Fine-Tuning an Existing Model
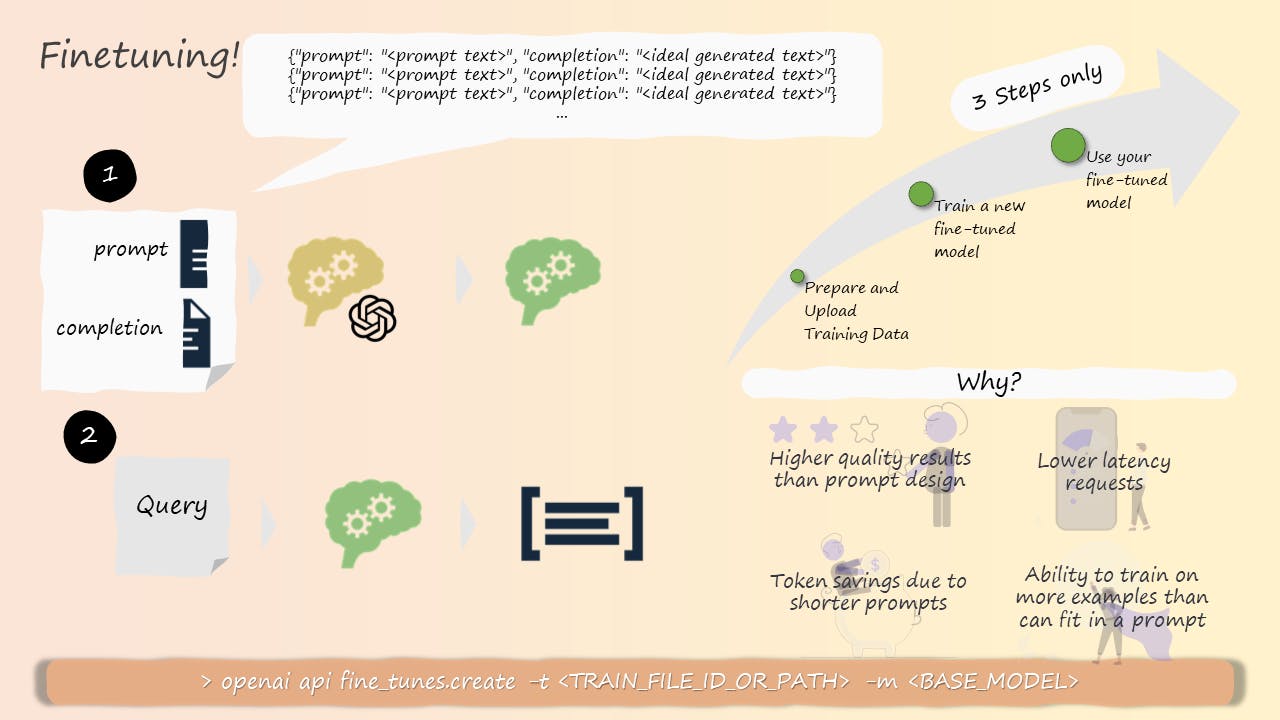
This adapts a model like GPT-3 to your domain by continuing its training on your data. Fine-tuning is more efficient than building from scratch but still expensive, and it risks "catastrophic forgetting" where the model loses knowledge from its pretraining. Fine-tuning also does not guarantee factual correctness. However, there are also some techniques to mitigate these drawbacks, such as Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF), which involves using human feedback to guide the finetuning process and improve the model’s quality and robustness. RLHF can also reduce the amount of data and resources needed for finetuning. For example, ChatGPT is trained to interact in a conversational way using Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), allowing it to answer follow-up questions, admit its mistakes, challenge incorrect premises, and reject inappropriate requests
Pros ✅:
Leverages the power of pretrained LLMs
Can improve performance on specific tasks or domains
Cons ❌:
Risk of hallucinations or generating irrelevant outputs
May not preserve factual correctness
Requires access to large amounts of labeled data
Access control and cost concerns
Method 3: Implementing a Retrieval-Augmented Language Model (REALM)
This involves separating your knowledge from the LLM. You find relevant documents for the user's question and generate prompts from those documents to send to the LLM. The LLM then responds based on its understanding of the prompts. This leverages the LLM's capabilities while providing accurate, traceable responses. However, it requires data processing to generate effective prompts.
Pros ✅:
Separates knowledge from the LLM, leveraging the LLM's semantic understanding
Provides accurate and traceable answers
Can access external documents for supporting knowledge
Cons ❌:
- Requires chunking and splitting data, indexing and ranking documents, and generating effective prompts
Deep Dive: Retrieval-Augmented Language Models

A Retrieval-Augmented Language Model or REALM is a method that integrates a knowledge retriever into a language representation model. This allows the model to access external documents as supporting knowledge for answering questions.
How does REALM work?
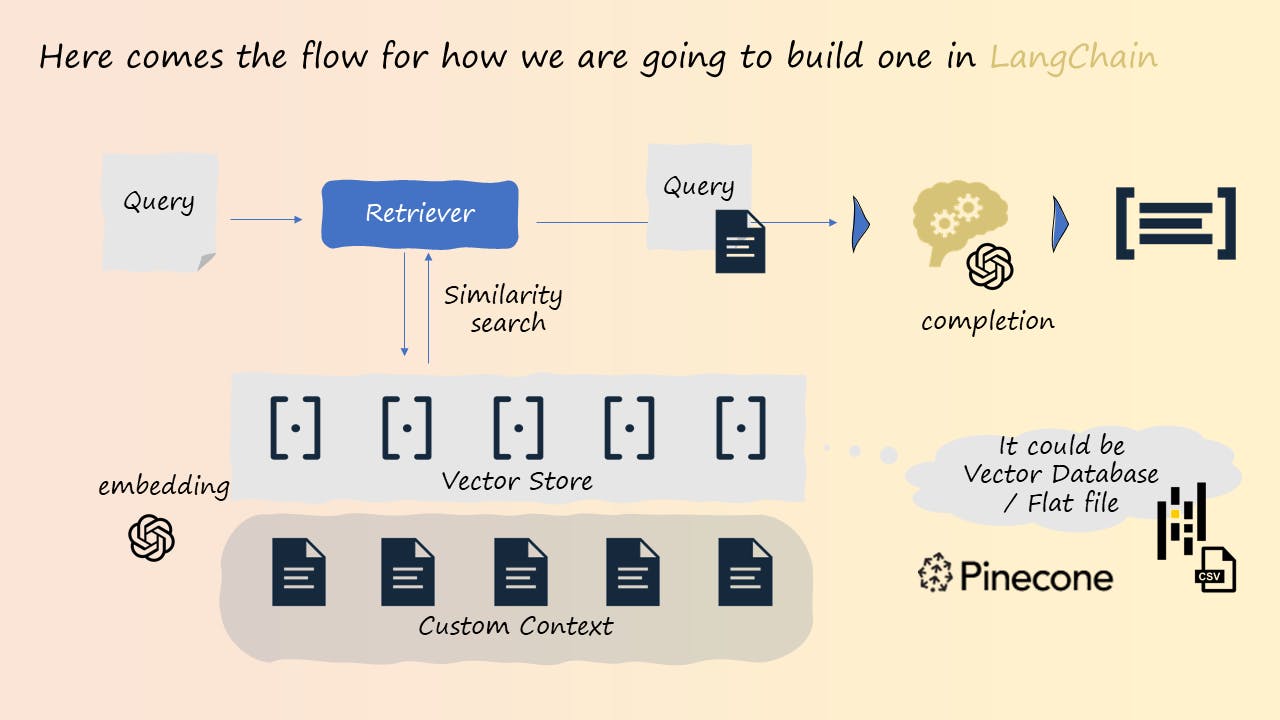
The process of implementing a REALM involves the following steps:
Chunking and splitting data: Break down your custom dataset into smaller, manageable pieces that can be easily retrieved and utilized by the model.
Indexing and ranking documents: Create an index of the documents in your dataset to enable efficient retrieval. Implement a ranking mechanism to select the most relevant documents for a given query. This step includes using a vector database that stores embeddings of the documents in a high-dimensional space, allowing for fast similarity search based on cosine similarity (or other similarity algorithms).
Generating effective prompts: Craft prompts for the LLM that incorporate the retrieved documents, allowing the LLM to leverage its semantic understanding and provide accurate, traceable answers.
For example, given a question like "When was Albert Einstein born?", REALM would first retrieve Einstein's biography from its index of documents. It would then send a prompt summarizing this information to the LLM, e.g. "Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879 in Ulm, Germany." The LLM can then respond based on this prompt, saying "Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879."
Vector Database is on 🔥
A vector database is an important component of REALM as it facilitates efficient retrieval of relevant documents. The vector database stores embeddings of the documents in a high-dimensional space, allowing for fast similarity search based on cosine similarity. This is how it works:
When a query is made, the query is also embedded in the same space as the documents.
The most similar documents are retrieved based on their proximity to the query vector.
The ranking mechanism selects the most relevant documents for a given query.
Using a vector database can significantly speed up the retrieval process and improve the overall performance of the REALM model. By using a vector database, LLMs can also improve their text generation quality and diversity in the following ways:
They can leverage the semantic information stored in the vectors to generate more relevant and coherent text based on a AI skill.
They can avoid generating inaccurate or irrelevant information by checking the factual consistency or common sense of their generated text against the vector database.
They can reduce the repetition or contradiction of their generated text by keeping track of the previous vectors they have used or generated.
They can mitigate the bias or offensiveness of their generated text by filtering out the vectors that are associated with harmful or inappropriate data.
Vector databases are therefore essential tools for enabling LLMs to generate more relevant and coherent text based on a AI skill. They provide a way to store and retrieve semantic information that can enhance the natural language understanding and generation capabilities of LLMs. Vector databases are also scalable and flexible, allowing LLMs to handle various types and sizes of data and queries.
Why use REALM?
REALM has several benefits over fine-tuning an LLM on a fixed corpus of documents. Here are some of them:
Mitigates risks: REALM avoids the problems of catastrophic forgetting and hallucinations that can occur when fine-tuning an LLM. Because it retrieves knowledge from documents, its responses are always grounded in evidence.
Provides more control and interpretability: REALM gives more flexibility and transparency to the user. Because it retrieves knowledge from documents, its responses can be traced back to their sources. This enables features like response provenance, where the model shows which documents and passages supported its answer.
Improves performance: REALM has been shown to outperform standard LLMs on open-domain question-answering tasks, making it a powerful approach for ingesting custom knowledge into LLMs.
How to get started with REALM?
If you are interested in using REALM for your own projects, you can check out some of the resources below:
- REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training: The original paper that introduces REALM and its architecture

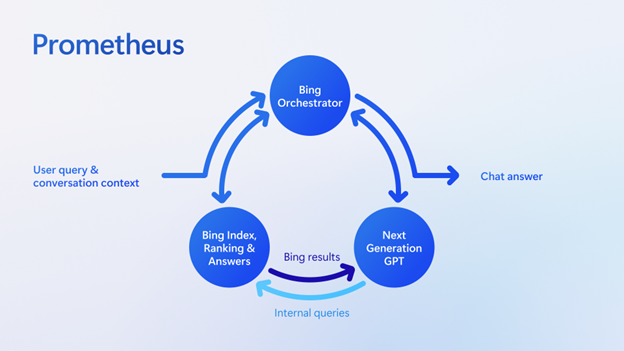
- Building the New Bing | Search Quality Insights: Jordi Ribas CVP at Microsoft – Search & AI talks about the New Bing and Microsoft Prometheus model
LangChain: a framework for developing applications powered by language models. It allows users to create data-aware and agentic applications that can interact with their environment and other sources of data. LangChain provides modular components, use-case specific chains, and agent simulations to help users build and deploy their own language model applications. LangChain supports Python and JavaScript languages and integrates with various model types and platforms
Google’s Project Tailwind https://blog.google/technology/ai/google-labs-sign-up/
I hope this blog post has given you some insights into what REALM is and how it can help you enhance your LLMs with external knowledge. If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment below or send me a message on LinkedIn! 📩. Happy coding! 😊

